Dectomax™ Injection for Sheep

Dectomax™ Injection for Sheep
Dectomax Injection is a group 3, ML (clear) wormer containing doramectin, that treats worms and scab in sheep with a single intramuscular injection. It can be used as part of a quarantine dose for incoming stock to treat for worms and scab.
Key Features
- Use in a sheep scab and worm control programme
- Use as a quarantine dose for incoming stock
- Is effective against group 1-resistant worms
Packs available
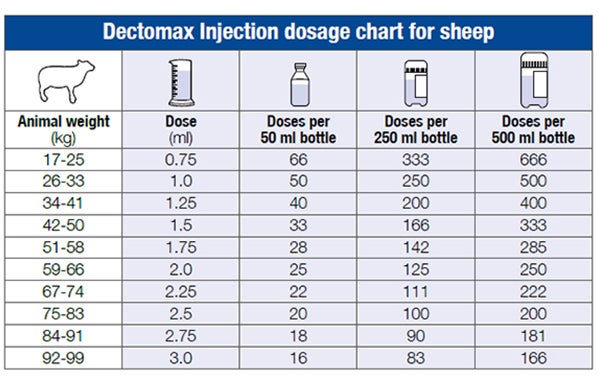
Dectomax Injection is available in the following bottle sizes: 50ml ; 250ml ; 500ml
Dectomax Injection for Sheep Product Information
Target activity
Dosage
Administration
Withdrawal periods
Target activity of Dectomax Injection for Sheep
Dectomax Injection treats and controls infections of gastrointestinal roundworms, lungworms, nasal bots and mange mites in sheep:
- Gastrointestinal roundworms (adults and fourth stage larvae)
- Chabertia ovina (adults only)
- Cooperia curticei (L4 only)
- Cooperia oncophora
- Gaigeria pachycelis
- Haemonchus contortus
- Nematodirus battus (L4 only)*
- Ostertagia (Teladorsagia) circumcincta**
- Oesophagostomum columbianum
- Strongyloides papillosus
- Trichostrongylus axei
- T. colubriformis
- T. vitrinus
- Trichuris spp (adults only)
*For effective treatment and control of both adults and L4 larvae of Nematodirus battus a dose rate of 300mcg/kg is needed.
**Inhibited larval stages (L4) including strains that are resistant to benzimidazole are also controlled
Lungworms (adults and fourth stage larvae): Dictyocaulus filaria (adults only)
Nasal bots (1st, 2nd and 3rd instar larvae): Oestrus ovis
Mange mites: Psoroptes ovis
Special warnings
Care should be taken to avoid the following practices because they increase the risk of development of resistance and could ultimately result in ineffective therapy:
Too frequent and repeated use of anthelmintics from the same class, over an extended period of time.
Underdosing, which may be due to underestimation of bodyweight, misadministration of Dectomax Injection, or lack of calibration of the dosing device.
Suspected clinical cases of resistance to anthelmintics should be further investigated using appropriate tests (Faecal Egg Count Reduction Tests). Where the results of the test(s) strongly suggest resistance to a particular anthelmintic, an anthelmintic belonging to another pharmacological class and having a different mode of action should be used.
Special precautions for use in animals
Dectomax Injection does not contain an antimicrobial preservative. Swab the septum before removing each dose. Use sterile equipment and follow aseptic procedures.
When treating groups of animals, use only the Dectomax automatic dosing device and vented draw-off apparatus.
For the treatment of individual sheep, a disposable 2ml syringe calibrated in increments of 0.1ml should be used.
In young lambs of less than 16kg bodyweight, seek veterinary advice regarding the use of appropriately sized needles and of 1ml disposable syringes graduated in increments of 0.1ml or less.
Syringes must be filled from the vial through a dry, sterile draw-off needle that has been placed in the vial stopper. Vial stoppers must not be broached more than 20 times.
Special precautions to be taken by the person administering Dectomax Injection to animals.
Do not eat, drink or smoke whilst handling the product. Wash hands and exposed skin after use. Take care to avoid accidental self-administration – seek medical attention if any specific signs are noticed.
Advice to medical practitioners: in cases of accidental self-administration, specific symptoms have rarely been observed and therefore any cases should be treated symptomatically.
Other precautions
Doramectin is very toxic to dung fauna and aquatic organisms and may accumulate in sediments. The risks to aquatic organisms and dung fauna can be reduced by avoiding too frequent and repeated use of doramectin (and products of the same anthelmintic class) in sheep.